Remote work tips
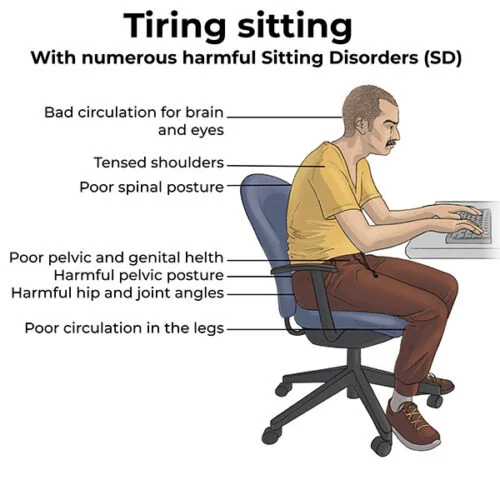
According to studies, productivity in remote work is 5 % lower than in the office. Poor productivity is mainly due to the bad ergonomics of “kitchen table & laptop”-level setups and the resulting sitting-related issues, leading to discomfort while working on the computer.
Looking down at a small laptop screen the following problems occur, and will just worsen over time.
- poor posture reduces breathing
- tightness in the neck muscles hinders blood circulation to the brain
- the position locks the shoulders
- intestinal functions slow down
- lower back is damaged
- circulation in the lower limbs is poor
- joints are compressed at incorrect angles
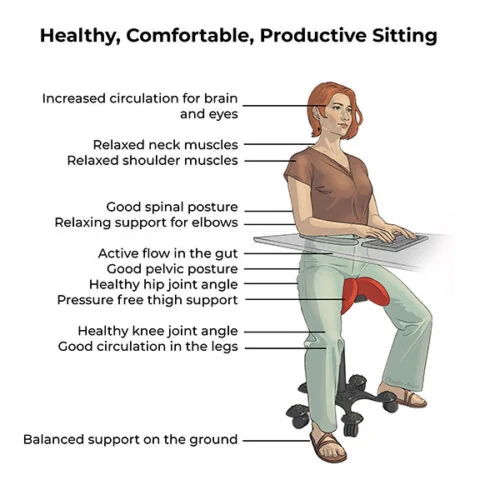
The best home office setup
The work station described below guarantees both good health and more productivity.
- A two-part Salli Saddle Chair, whose movement activates the tissues and organs in the pelvis and eliminates pressure from the pelvic floor area. If the swinging motion is not preferred, a tilting model is also available.
- An easily and quickly adjustable desk with a stomach recess and elbow pads, which relaxes the shoulders and arms.
- An Ultrawide monitor set at exactly the right height and distance, so the head does not need to hang or be pushed forward.
- Optimized lighting in the workspace. During dark hours, the use of a bright light lamp in the morning and forenoon adds vitality and adjusts the body’s circadian rhythm.
Further boost for your wellbeing at remote work
When the worker also wears loose and breathable clothes around the hips and moves a couple of times an hour, work productivity is much better than in the office using conventional furniture.
Maintaining stable blood sugar (avoiding fast carbohydrates), active intestinal function, good sleep, and a diet rich in fiber and nutrients help the brain achieve peak performance, keep energy levels high, and prevent negative feelings.
Supplements are also beneficial. It is advisable to take 3-4 g of Omega-3 fatty acids, 20 mg of zinc, 2 mg of copper, 200 mcg of selenium, 700 mg of magnesium, 100–150 mcg of vitamin D, 2–6 g of vitamin C, and 50 mg of vitamin E daily.
